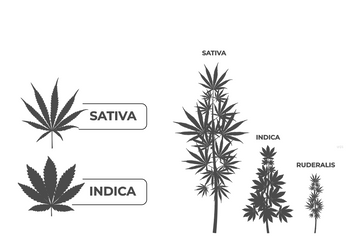
The BudTrainer Method™ Basics
Basics of Cannabis Home Cultivation
Written by cannabis production expert Henrique Dias - Edited on Sep 30,2024

DISCLAIMER: Everything taught and sold by BudTrainer® is to be used strictly for legal purposes. We condemn the production of illegal substances and it is your duty to ensure that you are complying with the law. The words "hemp", "cannabis", "weed", and "marijuana" are used interchangeably to refer to the same plant (legal hemp with less than 0.3% THC) for the purposes of this lesson.
Master the Basics & Grow Big Buds
Growing high-quality cannabis is nothing more than growing healthy plants. Plants that thrive and love their environment while producing top-shelf bud. And guess what? In order to grow healthy plants all you have to do is learn the basics about cannabis cultivation, and make sure that you don't screw up. In fact, 90% of growing cannabis is simply not screwing up. If you are growing for the first time, this lesson will teach you the basics of growing cannabis.
1. Growing Weed Indoors vs Outdoors
- Cost - which one is more expensive?
- Quality - which one yields better results?
- Schedule - how long do plants take to grow?
These questions are important because they will help you decide whether you are going to be growing indoors or outdoors. Let’s look at the differences between both.
1.1 Cost - Indoors vs Outdoors
Growing marijuana outdoors is a lot cheaper than growing indoors for one main reason: the sun is free and provides a lot of energy to your plants, yielding large amounts of weed at the end of the year. You can easily grow plants that yield ½lb to over 1lb of weed with as little as $100 per plant (pots, soil, nutrients, etc).
If you can grow 1 plant in your backyard with $100 and have a yield of up 1lb, this is the same as paying $0.22 per gram. Not to mention that for most people, 1lb of weed is more than enough for the whole year!

Growing marijuana indoors, on the other hand, costs more before AND after you start growing. A decent indoor setup that grows 1lb of cannabis every 4 months costs around $1,000, the electricity bill will come to around $200 per year, and everything else (nutrients, water, etc) adds another $200.
This means that, in the first year alone you are spending $1,400 for 3lb of weed. If we were to add nutrients and water to the bill, this means you are paying an average of $1.03 per gram in the first year, and as little as $0.30 per gram every year thereafter (compared to $0.22 from outdoors).

1.2 Quality - Indoors vs Outdoors
Growing cannabis outdoors is always dependent on the conditions of the environment around your plants. If it rains too much, your bud won’t be as good. If there are too many bugs or mold, your bud won’t be as good. If it is too dry, your bud won’t be as good. And so on. Basically, the quality (and thus the THC content) of your outdoor plants is directly proportional to the quality of your environment.
Since the environment outside is never consistent, this means that growing outdoors will always see a few bad days here and there, which inherently will compromise the quality and THC content of your bud.
In fact, most licensed commercial outdoor cannabis growers end up selling their cannabis for extraction since they don't pass the microbial tests required at the lab, and nor do they get the high-THC levels that indoors cannabis does.

Growing cannabis indoors, on the other hand, removes all of the problems that the outdoors environment creates. When growing marijuana indoors you can set a consistent temperature and humidity, you can adjust the height of your lights, and your plants are never at the mercy of the weather.
A controlled environment is always better for cannabis, which is why growing indoors yields the best and cleanest results, and as such more potent and higher quality bud.

1.3 Schedule - Indoors vs Outdoors
Growing weed outdoors requires you to stick to the schedule of the sun. In Northern US States and Canada, the earliest you can safely plant marijuana plants outdoors is May, and the latest you should harvest is at the end of October. As a rule of thumb, if it is below 50F/10C outside then it is too cold for your plants.

Growing weed indoors, however, puts the schedule fully under your control and you never depend on the season to grow. You can start and finish your plants whenever you want, and you can also grow during the Winter months. This allows you to get 3 or 4 harvests per year in a single grow tent, under your own terms.
3. Vegetative vs Flowering Stages
Did you know that marijuana has two stages of growth - one for growing only branches and leaves and another for only growing flowers (i.e. bud)? That’s right! Unlike tomatoes, which grow branches, leaves, and fruit at the same time, cannabis plants can only do one thing at once: either grow branches and leaves (called the vegetative stage), or grow flowers AKA bud (called the flowering stage).
What causes weed plants to switch from the vegetative stage to the flowering stage is the availability of light AKA photoperiodism. When cannabis plants get 16h or more of light per day, they stay in the veg stage. However, when they get 12h of light or less, they automatically switch to the flowering stage and start producing buds. Let’s understand why.
3.1 Veg to Flower Natural Switch
When days are long and the nights are short, weed plants think that it’s Spring and Summer time, so they only grow branches and leaves in order to gain as much size as possible.
However, as Fall approaches and the days get shorter, cannabis plants realize Winter is coming to kill them, so they switch to the flowering stage (around August), when they only grow flowers in order to reproduce and make seeds before they die of cold. It’s a smart strategy for them: grow when there is light, reproduce when there isn’t.
The plants below are both in the veg stage, growing only branches and leaves, branches and leaves.

3.2 Veg to Flower Artificial Switch
What photoperiodism means for growing cannabis indoors is that if you leave your lights on for 18h and off for 6h, your plants will think it’s Spring and stay in the veg stage. You can stay in the vegetative stage for as long or as short as you would like, as long as the lights are in the 18h/6h schedule. In the BudTrainer method we recommend staying in the veg stage for 6 to 8 weeks, but if you want to grow massive plants or do a canna bonsai, you can leave your lights on for 18h/day for multiple months.
In order to flip your indoor marijuana plants to flower, simply switch your light schedule from 18h/6h to 12h on and 12h off every day. Your plants will be tricked into thinking it’s Fall time, and will start producing flowers instead of branches and leaves only. The flowering period, different from the veg stage, doesn’t last indefinitely - in 8 to 12 weeks your plants will be ready for harvest (depending on which strain you are growing).
However, there is one exception to photoperiodism: autoflowers.

Behind the Leaves: How do Autoflowers Flower?
While some regions of the world have very short days in the Winter and long days in the Summer (e.g. Greenland), other regions have almost the same day-length all year long (e.g.. Thailand).
Since the switch from Summer to Fall is too fast in regions far North and South (i.e. it goes from hot to cold very quickly), cannabis plants that grow in those regions don’t have time to wait for the days to become short in order to start flowering - they must do it while the days are still long, or they will end up frozen in Winter before they could mature their seeds.
Conversely, strains that are too close to the equator can’t rely on day length to flower because every day has 12h of light and 12h of dark, all year long. Because of this, autoflowering cannabis plants had to rely on a system called the C:N ratio in order to flower. Let’s see how it works.
The C:N Ratio
The Carbon to Nitrogen Ratio (C:N Ratio) is a phenomenon that triggers the flowering cycle on plants, just like changing light cycles does. More precisely, this happens after the amount of assimilated carbon (C) in the plant compared to nitrogen (N) surpasses a certain threshold.
When this ratio is high enough, it means your plant has stored enough sugars (Carbon = Carbohydrates) in relation to leaves (Nitrogen) to start the flower cycle and sustain those flowers until it dies.
It’s as if your plants said: my tanks are full of sugars and I can get all the way to the end of the flower stage with this much energy. And so they flower. The autoflower below just started showing it's very first white pistils on the top node.

6. Feminized Marijuana Seeds
Most cannabis seeds are non-feminized, meaning you have no idea whether what you are planting is a male or a female plant. You always have to wait until your plants flower in order to tell which is which.
Feminized seeds, on the other hand, are seeds that always yield female plants. Instead of risking your plant being born a male, feminized seeds remove that risk altogether. While they are more expensive than regular seeds, feminized seeds are worth every penny because there is nothing worse than growing a male plant for weeks, finding out it is a male after it has flowered, and then having to throw it out in the garbage.

You Are Off To A Great Start
Now that you know the basics of cannabis growing, it’s time to get your seeds picked and planted!If you are ready to learn the best way to plant (and transplant) cannabis seeds, check out Lesson #1: How to Plant Cannabis Seeds.
Learn to Grow Big Buds
And be the first to hear about new articles, product releases, and special events.
About The Author

Henrique, the CEO of BudTrainer, is a mechanical engineer with a commercial cannabis production post-grad, and is also a former commercial cannabis consultant.
H takes plant science principles and breaks them down into simple steps for home growers to achieve the same results as the pros and grow the highest-quality cannabis.